| Genus List | Species List |
This key relies heavily on the character systems and structure developed by the late W. L. Brown, Jr. Every couple of years he would produce a new version of his New World Pachycondyla key, a few photocopies of which would escape and proliferate among myrmecologists (in spite of his warnings about its provisional nature). In a way, his system of photocopies with periodic upgrades, distasteful though it was to him, presaged Web-based documents such as this one. They are live, in-progress documents, subject to change, yet still very useful to myrmecologists.
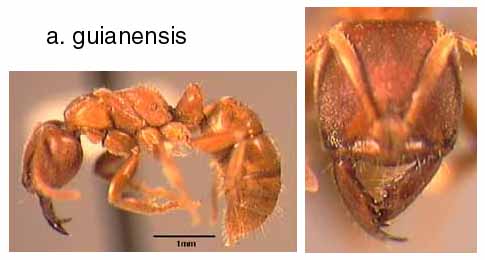
10a. Extensor surfaces of mid-tibiae with stiff, conical setae set over at least 1/2 of their length (figure); yellowish in color; eyes absent; mandibles sublinear, oblique masticatory border continuous with basal border: guianensis
10b. Extensor surfaces of mid-tibiae without stiff, conical setae, though long, fine erect setae may occur; orange to black in color; eyes small or large but distinctly present and multifacetted; mandibles usually triangular, with basal and masticatory borders meeting at a distinct angle (but not in the common tramp species stigma): 20

20a. Large black ants with dorsum of mesosoma and propodeum devoid of erect hairs; body surface sericeous; active surface foragers with rapid, nervous, wasp-like behavior: 30
20b. Dorsum of mesosoma and propodeum with erect hairs; size, color, and body surface various; behavior not nervous and wasp-like: 50
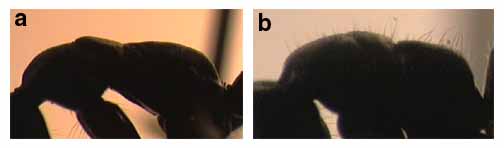
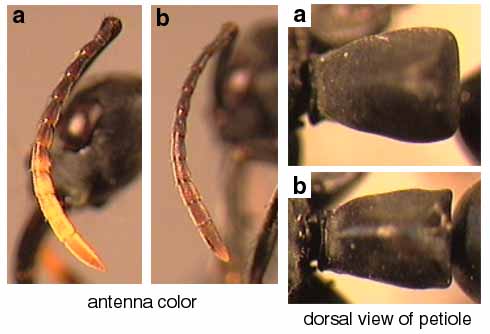
30a. Tips of antennae bright yellow; posterolateral margins of petiole feebly margined (apicalis and verenae are remarkably similar species, but are broadly sympatric and occur together in forested habitats): apicalis
30b. Tips of antennae brown; posterolateral margins of petiole distinctly, although not sharply, margined: verenae
50a. Opening of propodeal spiracle viewed perpendicularly small and round: 60
50b. Opening of propodeal spiracle viewed perpendicularly slit-shaped, more than twice as long as wide (spiracle may be very small, and boss around spiracle may be round, but actual orifice still slit-shaped): 100

60a. Clypeus truncate anteriorly; posteroventral margin of petiole with flat, posteriorly directed flange that extends almost to posterior margin of petiole: 63
60b. Clypeus subtriangular anteriorly; ventral margin of petiole with anteroventral lobe which may be square-cut posteriorly, but without a posteriorly projecting flange: 70

63a. Base of mandible with pronounced curving sulcus; petiolar node cuboidal in side view, not tapering dorsally: 65
63b. Base of mandible with sulcus indistinct or absent; petiolar node often more tapered dorsally: 67
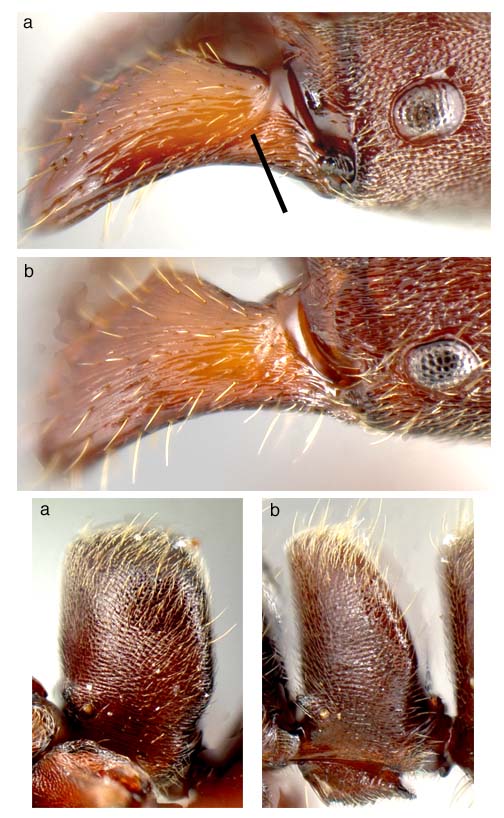
65a. Surface of mandible striate; sides of head with no or very sparse erect setae; petiole relatively broad in side view: panamensis
65b. Surface of mandible smooth and shining; sides of head with abundant erect setae; petiole relatively narrower in side view: JTL-018
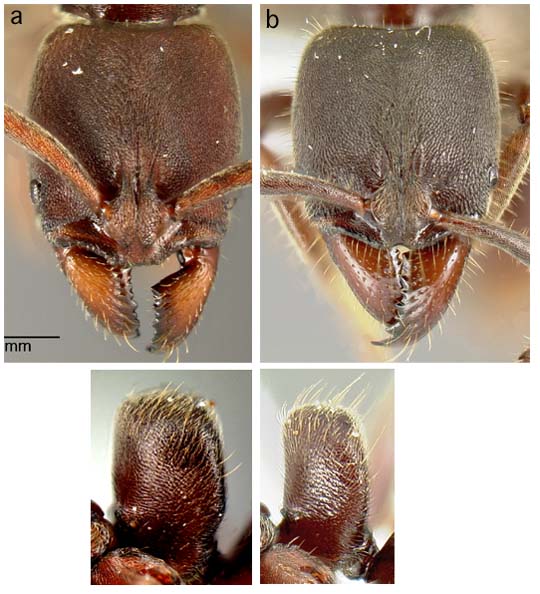

67a. Mandibles striate; pubescence of third abdominal tergite relatively dense, scruffy; often with short erect setae on hind tibia; head width variable; nests under dead wood or stones on the ground: 68
67b. Mandibles smooth and shining or very faintly striate; pubescence of third abdominal tergite relatively dilute, shorter; hind tibia with no erect setae; head width 1.28-1.41mm; nests under epiphytes: JTL-014

68a. Petiole in side view cuboidal, with parallel anterior and posterior faces; head width 1.08mm (n=1): JTL-017
68b. Petiole in side view tapering dorsally; head width variable: 69

69a. Petiole less tapering in side view; size smaller, head width about 0.90mm; color lighter orange brown: JTL-016
69b. Petiole more tapering; size larger, head width about 1.07mm; color darker red brown: JTL-015

70a. Propodeal suture deeply impressed; scapes extend far beyond vertex margin: constricta
70b. Propodeal suture not deeply impressed; scapes barely reach vertex margin: 75
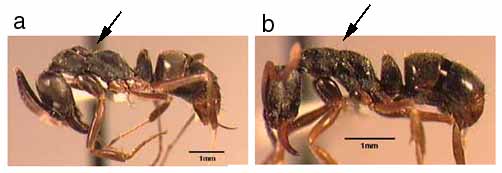
75a. Ventral petiolar process with a low, square-cut posterior margin; sides of head lacking erect setae; dorsal and lateral faces of pronotum separated by a feeble, rounded margin: arhuaca
75b. Ventral petiolar process broadly convex, posterior margin rounded; sides of head with projecting erect setae; dorsal and lateral faces of pronotum continuous, not differentiated: 80

80a. Anteromedian margin of clypeus with a short spine: becculata
80b. Anteromedian margin of clypeus triangular, lacking spine: pergandei
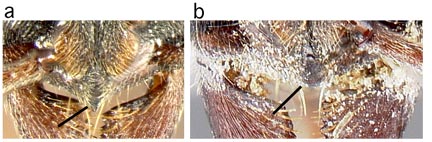
100a. Black; very smooth and shining, forming a highly polished, reflective surface over most of body: laevigata
100b. Color various; body never strongly shining over most of surface; surface largely mat with various degrees of punctation or striation: 110

110a. Mandible with 6-8 teeth; head width less than 1.3mm; petiole scale-shaped, tapering dorsally to rounded summit (stigma complex): 120
110b. Mandible with 9 or more teeth; head width usually greater than 1.3mm; petiole shape various: 200
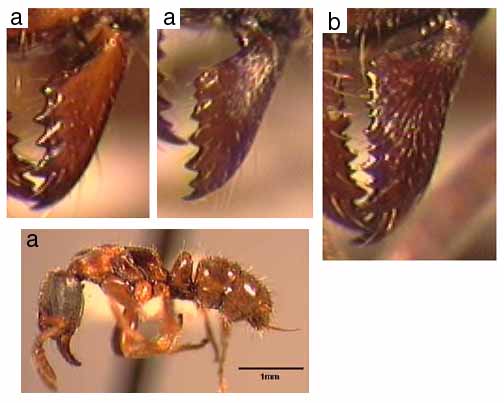
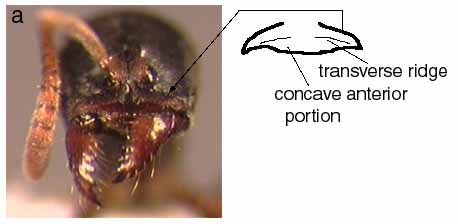
120a. Lateral wings of clypeus divided by distinct transverse ridge, anterior portion distinctly concave and bent ventrad; in lateral profile, posterior margin of anteroventral petiolar lobe subangular to square-cut or even slightly produced as a subacute angle; mandible with 6 or 7 teeth (non-tramp species of mature forest habitats): 130
120b. Lateral wings of clypeus almost smoothly convex, transverse ridge very weak, anterior portion flat to weakly concave, not as strongly bent ventrad as above; in lateral profile, posterior margin of anteroventral petiolar lobe broadly rounded; mandible with 6 teeth, basal and masticatory margins not well-differentiated (common tramp species in disturbed areas; less often in mature forest): stigma
130a. Frontal carinae not closely approximated where they accomodate scapes, ratio of greatest distance between frontal carinae (across frontal lobes) to smallest distance 2.5: 140
130b. Frontal carinae closely approximated, ratio of greatest distance between frontal carinae to smallest distance 5.5: cognata
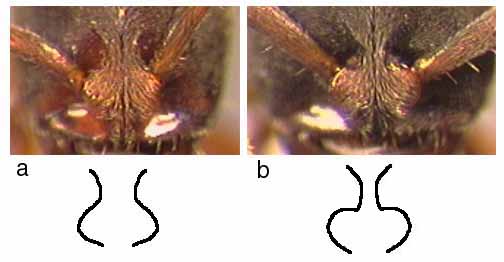
140a. Mandible usually with 6 teeth, basal and masticatory margins not well-differentiated: cauta
140b. Mandible with 7 or 8 teeth, basal and masticatory margin relatively more differentiated: gilloglyi

200a. In side view, dorsal outline of mesosoma forms a continuous convexity including mesonotum, metanotum and propodeal dorsum; propodeal groove obsolete or nearly so, and not strongly impressed; pronotal dorsum usually with strong, lateral margins: 210
200b. Dorsal outline of mesosoma interrupted by a distinct, impressed propodeal groove, so that the mesonotum forms a convexity separate from the more or less convex propodeal dorsum; lateral margins of pronotal dorsum distinct, indistinct, or absent: 350
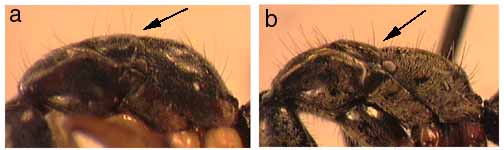
210a. A distinct carina runs from the lateral wing of the clypeus near the mandibular insertion to or nearly to the anteromesal quarter of the margin around the eye; acrotergite of second gastral tergum (when exposed) with a distinctly differentiated median stridulatory file with bands of rainbow colors; arolia present (figure): 220
210b. Cheeks without a distinct carina reaching more than halfway from clypeal wing to eye margin (a carina indistinct from the background sculpture may sometimes occur); stridulatory file absent; arolia absent: 300
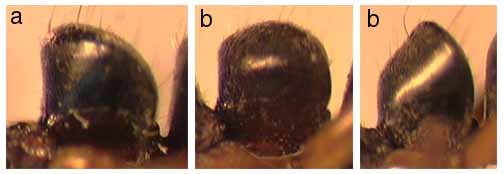
220a. Petiolar node as seen from the side with front face rising abruptly to an angular summit at or near the front, from which it descends behind through a broad curve: 230
220b. Petiolar node as seen from the side with a horizontal or strongly rounded summit with highest point near nodal midlength; or else the apex rises well behind midlength: 250
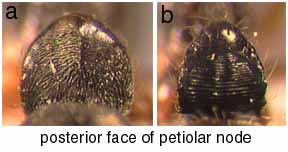
230a. Posterior face of petiolar node densely and finely punctulate, not striate: unidentata complex (antecurvata, rugosula, unidentata)
230b. Posterior face of petiolar node coarsely transversely striate over most or all of surface: striatinodis
250a. Petiolar node as seen from the side more or less subquadrate, with vertical anterior and posterior faces and a horizontal but convex dorsal face: 255
250b. Petiolar node as seen from the side with anterior and posterior faces strongly converging above to form a sharply rounded summit near midlength: carinulata
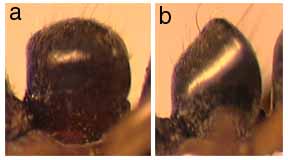
255a. Color orange; antennal scapes when laid back just reach margin of vertex; size smaller: crenata
255b. Color black; antennal scapes long, distinctly surpassing margin of vertex; size larger: JTL-013
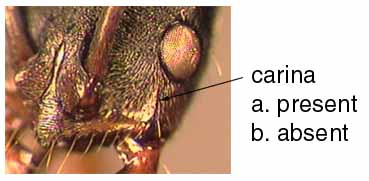
300a. Head width less than 2.0mm; mesosoma less than 3.6mm long; dorsolateral margin of pronotum often with a distinct carina (figure): harpax complex
300b. Head width greater than 2.0mm; mesosoma greater than 3.6mm long; dorsolateral margin of pronotum uniformly punctate, rounded: 320
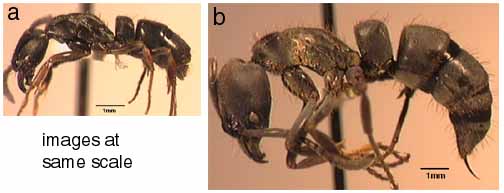
320a. Clypeus narrow front to back, with deep median notch that extends almost to anterior margins of frontal lobes: impressa
320b. Clypeus broader front to back, anterior margin truncate, flattened to weakly notched, but with medial margin well in front of frontal lobes: purpurascens
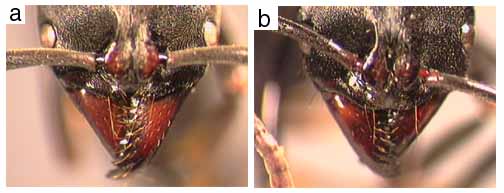
350a. In full-face view, a line drawn through the centers of the eyes falls near mid-head, crossing near posterior limits of frontal carinae; cheeks usually with a distinct carina reaching from clypeal wing to eye margin: 360
350b. Eyes situated more anteriorly on head, such that a line drawn through the centers of the eyes crosses the frontal carinae near their greatest constriction; cheeks without a distinct carina reaching from clypeal wing to eye margin (montane species): aenescens
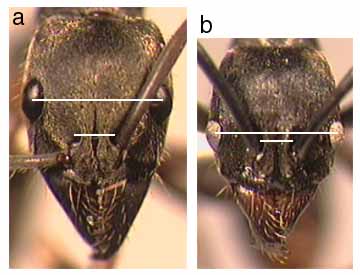
360a. Anterior face of petiolar node somewhat sloping to rounded apex: 365
360b. Anterior face of petiolar node more perpendicular, forming a more angular anterodorsal summit: 370
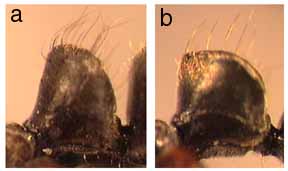
365a. Dorsolateral margins of petiole absent; slender species with posterior margin of head straight to feebly convex in full-face view; antennal scapes long, SI greater than 120: dismarginata
365b. Dorsolateral margins of petiole present; posterior margin of head broadly and strongly convex; antennal scapes relatively shorter, SI less than 120: JTL-012
370a. Center of vertex convex, covered with very coarse, diverging-longitudinal striation, free of pubescence, shining and contrasting strongly with the surrounding areas of fine sculpture and pubescence; center of posterior face of node usually coarsely vertically rugose: lineaticeps
370b. Vertex with sculpture and pubescence like most of remaining dorsum of head, punctulate or finely striate; posterior face of node sculptured differently -- transversely striate or with indefinitely oriented rugosity or punctulae: 380

380a. Posterior face of petiolar node coarsely, transversely striate to apex; head width including eyes greater than 2.0mm: foetida
380b. Upper half of posterior face of petiolar node finely punctulate or otherwise sculptured, not transversely striate; other characters various: 390
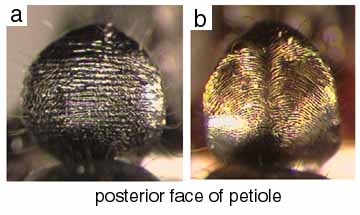
390a. Sides of petiolar node longitudinally striate or rugulose on the lower half or more; often irregularly striate or rugulose on lower part of posterior face as well: theresiae
390b. Sides of node finely punctulate, surface weakly shining: 400
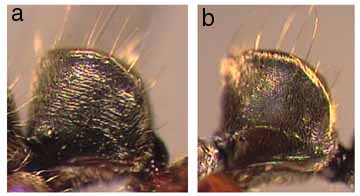
400a. Anteromedian portion of clypeus transversely rugose: insignis
400b. Anteromedian portion of clypeus smooth or longitudinally striatorugose: 410
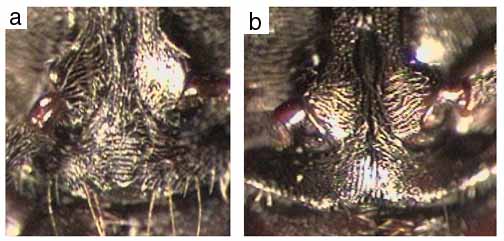
410a. Larger, more robust species, head width including eyes usually greater than 2.2mm, width of pronotum greater than 1.55mm: villosa
410b. Smaller and more slender species, head width including eyes usually less than 2.2mm, width of pronotum less than 1.55mm: bugabensis
Page author:
John T. Longino, The Evergreen State College, Olympia WA 98505 USA.longinoj@evergreen.edu